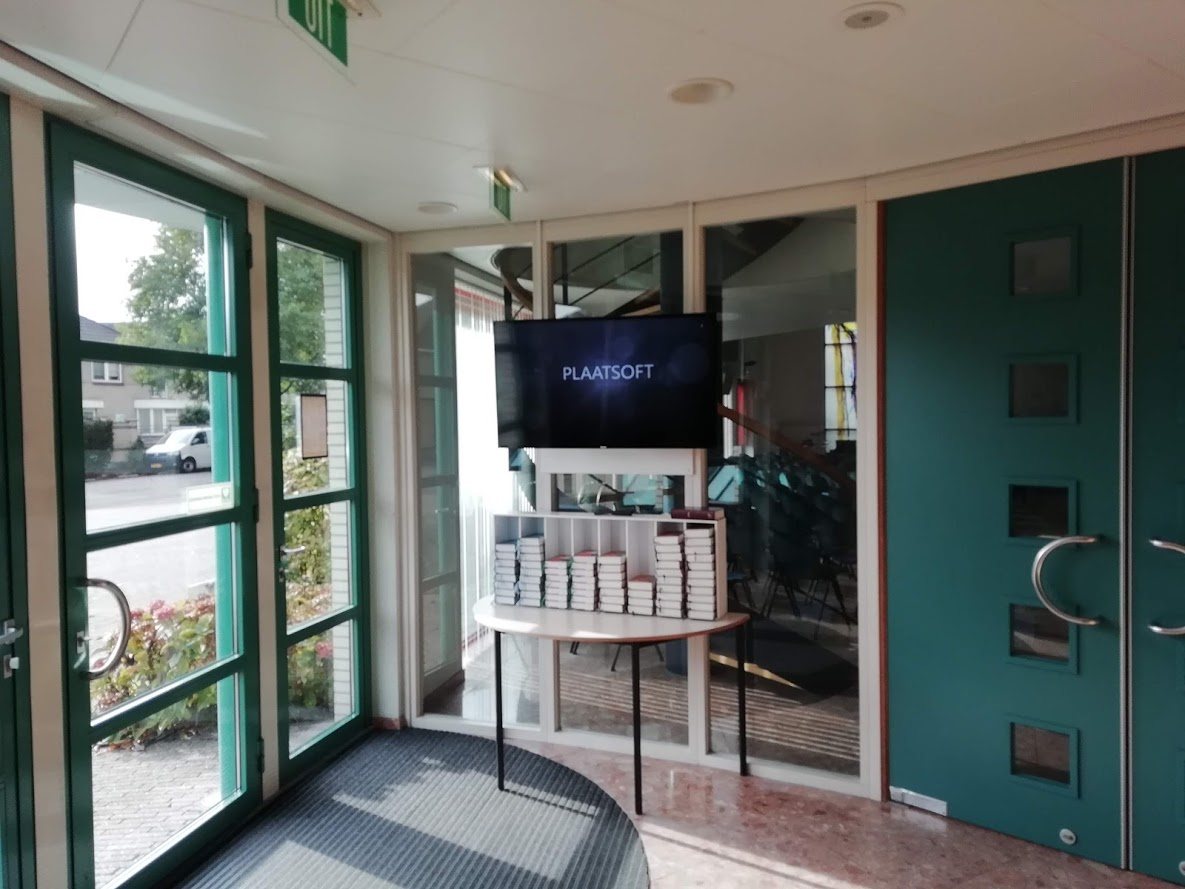

PlaatSoft software (PlaatSign and PlaatEnergy) runs on two Raspberry Pi’s in a Dutch Church “De Oostpoort” in Gouda. The created information system will provide church visitors realtime information about the energy use and energy production (more then 100 solar panels are installed on the roof) of the church building.
Author: wplaat
New website Look-and-Feel
Today this website has been renewed. The layout has been given a modern dark look. The website is now also suitable for tablets and smartphones. Depending on the device type, the look and feel of the information is adjusted. In the short term, the server hardware on which this website is running will also be modernized so that the interaction is also accelerated.
Raspberry Pi Tower

My Raspberry Pi Tower is growing steadily. At this moment I have 4 Raspberry Pi’s (mini computer) running. One Pi is designed as an Access Point to the Internet and provides the SSL offloading. Furthermore, he routes the HTTP traffic via an Apache Reverse Proxy to the underlying three Pi’s. These Pi’s are arranged as web server and provide 22 websites. The advantage of this solution is that the total energy consumption (including gigabit switch) is approximately 30 Watt and the websites still provide a good response.
The following domains are hosted on the above hardware. Each domain also has a number of subdomains
PlaatSoft.nl
PlaatResort.nl
WarQuest.nl
KerkInGouda.nl
StichtingOpenHuisGouda.nl
PlaatSoft Intro
PlaatSign 1.0
 The next version of PlaatSign is released and contain the following changes:
The next version of PlaatSign is released and contain the following changes:
- Added energy day consumption script
- Added energy month consumption script
- Added energy year consumption script
- Added gouda weatherstation script
- Added broodkruimels script
- Improve file use on disk
- Added feature to enable / disable content
- Added plaatenergy database settings to settings page
- Updated copyrights banner
- Added new version check
Click here to download the latest version.
PlaatEnergy 1.5
 The next version of PlaatEnergy is released and contain the following changes:
The next version of PlaatEnergy is released and contain the following changes:
– Added feature to edit manual solar month history
– Added cron backup script which aggregrate data older then 1 year
Click here to download the latest version.
PlaatEnergy 1.4
 The next version of PlaatEnergy is released and contain the following changes:
The next version of PlaatEnergy is released and contain the following changes:
– Added energy1_detail table to measure 3 phases (voltage, current and power) of 380VAC connection
– Added voltage day chart
– Added current day chart
– Added power day chart
– Added extra energy setting to switch on/off detail information
Click here to download the latest version.
PlaatResort
The last 12 months I was very busy designing and building a small chalet on an island (1300m2) in Reeuwijk, The Netherlands. That’s the reason that the PlaatSoft software development was on hold. The house project is almost finished, so i am back again.
For more information about the house project visit:
https://family.plaatsoft.nl
https://www.plaatresort.nl
Windows 10 upgrade takes hours
This afternoon my Quad Core 3GHZ Desktop finally received the Windows 10 creator patch. It took my desktop more than 4 hours to install it. Why is a Windows 10 patch always so slow? If i upgrade a Raspberry Pi Quad Core 1.2GHZ Linux kernel it’s only take 10 minutes. Strange that low end linux hardware upgrades are must faster than high end Windows hardware. I think that the Microsoft staff must go on training to learn how to patch Operating Systems fast and without reboots 🙂
Raspberry Pi Noobs cleanup
If you want to have a nice and clean Raspberry Pi Noobs installation. Execute te followings commands to remove unless tools:
sudo apt-get purge wolfram-engine (Reduce image size with 683MB)
sudo apt-get purge sonic-pi (Reduce image size with 151MB)
sudo apt-get purge scratch (Reduce image size with 93MB)
sudo apt-get purge scratch2 (Reduce image size with 147MB)
sudo apt-get purge scratch3 (Reduce image size with 147MB)
sudo apt-get autoclean
This initial Noobs image size will now be arround 4GB 🙂
WordPress upgrade
This afternoon I have upgraded my web server.
The following changes were implemented:
– WordPress is upgrade to 4.8.4
– All WordPress plugins are upgraded to latest available version.
Google Charts zoom in dataset example
 I took me a while to understand how Google Charts can be extended with a zoom/drill in data set feature. You have to add then google.visualization.events.addListener method which fetch the selected datapoint of a graph. With some extra javascript code you can reload the chart with a more detailed dataset. See example below!
I took me a while to understand how Google Charts can be extended with a zoom/drill in data set feature. You have to add then google.visualization.events.addListener method which fetch the selected datapoint of a graph. With some extra javascript code you can reload the chart with a more detailed dataset. See example below!
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.google.com/jsapi"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
google.load("visualization", "1", {packages:["bar"]});
google.setOnLoadCallback(drawChart);
function drawChart() {
var options = {
bars: "vertical",
bar: {groupWidth: "90%"},
legend: { position: "none"},
vAxis: {format: "decimal"},
isStacked:true,colors: ["#0066cc", "#808080"],vAxis: { format:"decimal", viewWindow: { min: 0, max: ".round($max_forecast+100)." } }, series: {
3: {
targetAxisIndex: 1
}
}
};
var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable([['','Low (kWh)','Normal (kWh)','Solar (kWh)','Forecast (kWh)'],['2006',0,0,0,0],['2007',0,0,0,0],['2008',0,0,0,0],['2009',0,0,0,0],['2010',0,0,0,0],['2011',0,0,0,0],['2012',0,0,0,0],['2013',0,0,0,0],['2014',0,0,0,0],['2015',0,0,0,0],['2016',20,20,11,278.75]]);
var chart = new google.charts.Bar(document.getElementById("chart_div"));
chart.draw(data, google.charts.Bar.convertOptions(options));
google.visualization.events.addListener(chart, "select", selectHandler);
function selectHandler(e) {
var year = data.getValue(chart.getSelection()[0].row, 0);
link("pid=30&eid=88&date="+year+"-1-1");
}
}
function link(value)
{
var form = document.forms['plaatenergy'];
var newInput = document.createElement('input');
newInput.setAttribute('type','hidden');
newInput.setAttribute('name','token');
newInput.setAttribute('value',value);
form.appendChild(newInput);
form.submit();
}
PlaatProtect 0.3
 This is the next release of PlaatProtect. The release contain the following changes and bug fixes:
This is the next release of PlaatProtect. The release contain the following changes and bug fixes:
– Improve new version detection script
– Improve php cron job. Now no output is created anymore
– Added battery chart for all zwave devices
– Added temperature chart for all zwave devices
– Added humidity chart for all zwave devices
– Added lumaniance chart for all zwave devices
– Added location of zwave sensors on home page
– Protect scenario and panic buttons against accidental click
– Bugfix: Fix critical bug in event.php in sleep and away mode
– Bugfix: Temperature above 25.5c is now correctly measured
Click here to download the latest version.
KnightsQuest 0.4.0
 This evening the next released of KnightQuest. It contain the following new features:
This evening the next released of KnightQuest. It contain the following new features:
– Added Mode Selector page.
– Added Player vs Player page.
– Added lots of sound effects.
– Sound effects can be switch on/off on settings page.
Click here to download the latest version.
Java KnightsQuest 0.3
 This evening the third beta is released of KnightQuest. It contain the following new features:
This evening the third beta is released of KnightQuest. It contain the following new features:
– Added 3 screen resolutions.
– Increase amount of maps to 60.
– Improve game play. Now maps must be unlocked.
– Pawn can now move two land tills per turn.
– Added harbors so soldiers can travel faster.
– Game settings and progress are now stored on disk.
– Bugfix: Second game initialization is working fine.
– Bugfix: Now autmatic next turn detection is working fine.
Click here to download the latest version.
Java KnightsQuest 0.2
 This evening the second beta is released of KnightQuest. It contain the following new features:
This evening the second beta is released of KnightQuest. It contain the following new features:
– Added human player functionality.
– Added information box on game screen.
– Improve bots behavior.
– Added new background.
– Improve help, credits, release notes and donate page.
– Added intro movie.
– Improve network detection.
– Music can now be switched off / on.
Click here to download the latest version.
Java KnightsQuest 0.1
 One week ago i start working on the game i want to create already for the last six years. Two attempts failed due to less time. I will try again now using JavaFx. So the game will support multiple Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, MacOS, etc..) out of the box. This is the first beta (not a full feature) release. Check it out. Comments are welcome!
One week ago i start working on the game i want to create already for the last six years. Two attempts failed due to less time. I will try again now using JavaFx. So the game will support multiple Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, MacOS, etc..) out of the box. This is the first beta (not a full feature) release. Check it out. Comments are welcome!
12-11-2016 Version 0.1
– Added basic game engine (only bot mode for now)
– Added six maps
– Added intro background music.
– Added new version detection,.
– Added help, credits, release notes and donate page.
– Added two intro pages with basic animation.
Click here to download the latest version.
Java RedSquare 0.3
 The third release of RedSquare for Java is released. The following change are made:
The third release of RedSquare for Java is released. The following change are made:
09-11-2016 Version 0.3
– Minor GUI update
– OPbfuscate classes
Click here to download the latest version.
PlaatSoft exist 20 years!
Twenty years ago the first PlaatSoft open source project was released on the internet. Its was a addressbook created in Borland Delphi. A lot have happend over the years. Many projects (Drupal Modules, Wii Games, Android Games, Windows Tools, Raspberry Pi tools, etc….) were created which received great feedback from users arround the world. Many thanks for using my software. I hope the next years will be just as must fun as the previous. Best Regards
Click here to find information about the first open source project.

Java RedSquare 0.2
 The second release of RedSquare for Java is released. This is the full feature release
The second release of RedSquare for Java is released. This is the full feature release
03-11-2016 Version 0.2
– Added setting page to control nickname.
– Protect blue squares against size hacking.
– Protect red square against size hacking.
– Added scrollbar to release notes page.
– Added CGI master hackers to credits page.
– Improve webservice calls.
– Check java version. If version is outdated, warn user
– Show warning when internet connection is down.
Click here to download the latest version.
tar bz2 commands
Extract:
tar xjvf bestand.tar.bz2
Create:
tar cjvf bestand.tar.bz2 file1.bmp file2.mp3 *.jpg
Patch Solaris
Download patch for http://sunsolve.sun.com
sftp patch to target
Patch Install:
unzip patch.zip
patchadd
Oracle SQL Loader
control file dwh.ctl
LOAD DATA
APPEND INTO TABLE CDR_UNRATED
(
WK_BMP_USAGE INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
WK_USAGE_TYPE INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
WK_EXCHANGE_ID INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
WK_TRANS_DT INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
WK_TRANS_TM INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
CDR_SEQUENCE_NUMBER INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
TRANS_DT DATE “ddmmyyyyhh24miss” TERMINATED BY “,”,
UNITS INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
RELATED_CALL_NUMBER INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
A_NUMBER CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
C_NUMBER CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
IN_SERVICE_IND CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
CALL_STATUS CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
MARKETING_CALL_STATUS CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
ANSWER_TIME INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
B_NUMBER CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
CHARGED_NUMBER CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
EXTERNAL_TYPE_ID INTEGER EXTERNAL TERMINATED BY “,”,
B_CATEGORY CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
SERVICE_TERMINATING CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
EXCEPTION_CODE CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”,
MEDIA_NUMBER CHAR TERMINATED BY “,”
)
CSV file
086,01,12345678912345,12345678912345,31122006,235959,1,31122006235959,12,0301234567,0301234567,10,U,A,5,182123451,282123451,1,15,I,abcdeabcdeabcde,1
Start SQL Loader
$ sqlldr TCT/TCT@ORCL control=dwh.ctl log=dwh_import.log data=DHW_20060501235959.csv
Create temporary database
CREATE GLOBAL TEMPORARY TABLE SELECTED_NUMBERS
( bnumber varchar2(50) not null)
on commit delete rows;
PRESERVE
Oracle Application Server commands
Oracle Application Server
Show Status
$ opmnctl status
Show Cluster status
$ opmnctl @cluster status
Stop single process
$ opmnctl stopproc -process-type=XXX
Start single process
$ opmnctl startproc -process-type=XXX
Stop all processes for a cluster
$ opmnctl @cluster stopall
Start all processes for a cluster
$ opmnctl @cluster startall
———————————————
Create new instance
$ createinstance – instanceName XXXX
$ opmnctl reload
$ opmnctl startall
Note: New instance will create a new group!
Remove instance
$ removeinstance -instanceName XXXX
———————————————-
Cluster IP address = 225.0.0.2
Cluster Port Number = 6790
———————————————-
