How to setup High Available PostgreSQL on two nodes.
Pi6 192.168.2.106 (MASTER)
Pi7 192.168.2.107 (REPLICATION)
Run below commands on both Pis:
sudo vi /etc/hosts
Add pi6 192.168.2.106
Add pi7 192.168.2.107
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get install postgresql
# Stop postgresql
sudo systemctl stop postgresql
# Create directories
sudo mkdir /data02
sudo mkdir /data02/data
sudo chmod a+wrx /data02
sudo chown postgres:postgres /data02/data
sudo chmod 0700 /data02/data
# Remove old databases
rm -rf /var/lib/postgresql/13/main
ln -s /data02/data /var/lib/postgresql/13/main
rm -rf /etc/postgresql/13/main
ln -s /data02/data /etc/postgresql/13/main
Run below commands only in Pi6 (MASTER):
# Create new database
/usr/lib/postgresql/13/bin/pg_ctl initdb -D /data02/data
# Update PostgresSQL configuration
vi /etc/postgresql/13/main/postgresql.conf
Change #listen_addresses = 'localhost' to listen_addresses = '*'
Change #wal_level = replica to wal_level = replica
Change #max_wal_senders = 10 to max_wal_senders = 10
Change #wal_keep_size = 0 to wal_keep_size = 0
vi /etc/postgresql/13/main/pg_hba.conf
Add next line
host all all 192.168.2.0/24 trust
host replication plaatsoft 192.168.2.0/24 trust
# Start database
/usr/lib/postgresql/13/bin/pg_ctl -D /data02/data start
of
systemctl start postgresql
# Create replication user
psql -c "CREATE USER plaatsoft WITH PASSWORD 'plaatsoft' REPLICATION;"
5. Create replication slot on Primary Server
psql -c "select * from pg_create_physical_replication_slot('standby1_slot');"
Run below commands only in Pi7 (REPLICATION):
# Create replication database based on master
/usr/lib/postgresql/13/bin/pg_basebackup --pgdata=/data02/data --format=p --write-recovery-conf --checkpoint=fast --label=mffb --progress --host=pi6 --port=5432 --username=plaatsoft
# Update PostgresSQL configuration
vi /etc/postgresql/13/main/postgresql.conf
# Update PostgresSQL configuration
vi /etc/postgresql/13/main/postgresql.conf
Change primary_conninfo to 'host=pi6 port=5432 user=plaatsoft password=plaatsoft'
Change primary_slot_name to 'standby1_slot'
# Start database
/usr/lib/postgresql/13/bin/pg_ctl -D /data02/data start
of
systemctl start postgresql
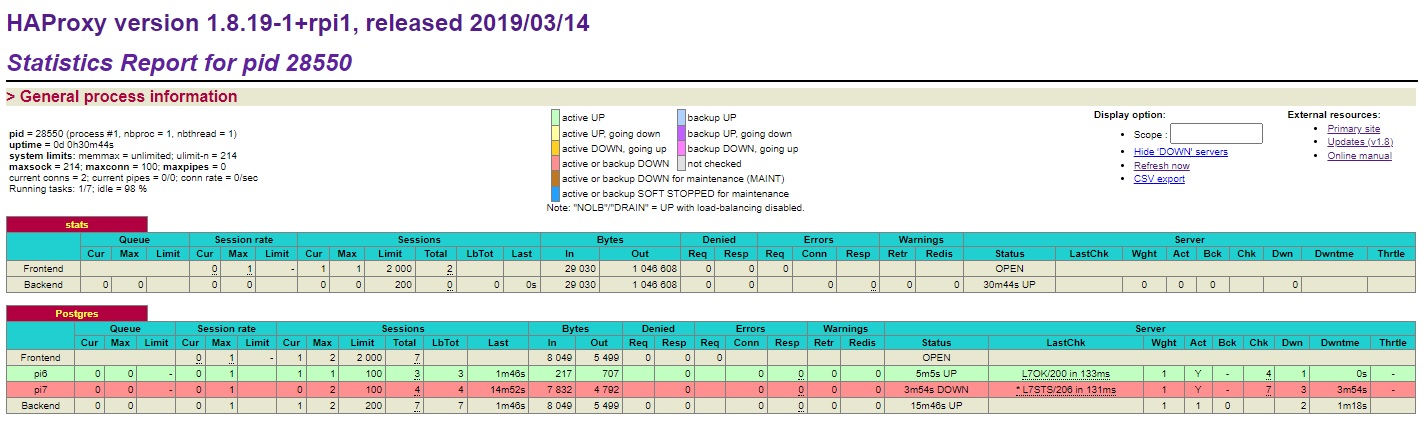
Final Check Pi6:
postgres 5211 1 0 13:04 ? 00:00:00 /usr/lib/postgresql/13/bin/postgres -D /data02/data
postgres 5215 5211 0 13:04 ? 00:00:00 postgres: checkpointer
postgres 5216 5211 0 13:04 ? 00:00:00 postgres: background writer
postgres 5218 5211 0 13:04 ? 00:00:00 postgres: walwriter
postgres 5219 5211 0 13:04 ? 00:00:00 postgres: autovacuum launcher
postgres 5220 5211 0 13:04 ? 00:00:00 postgres: stats collector
postgres 5221 5211 0 13:04 ? 00:00:00 postgres: logical replication launcher
postgres 5970 5211 0 13:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: walsender plaatsoft 192.168.2.107(46242) streaming 0/12013F58
Final Check Pi7:
postgres 23167 1 0 13:13 ? 00:00:00 /usr/lib/postgresql/13/bin/postgres -D /data02/data
postgres 23168 23167 0 13:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: startup recovering 000000010000000000000012
postgres 23169 23167 0 13:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: checkpointer
postgres 23170 23167 0 13:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: background writer
postgres 23171 23167 0 13:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: stats collector
postgres 23173 23167 0 13:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: walreceiver streaming 0/12013F58
![]() PlaatSoft has released a new version of PlaatDomotica.
PlaatSoft has released a new version of PlaatDomotica.

 Today there is a new update of WarQuest online!
Today there is a new update of WarQuest online!